Have you ever wondered exactly how old school children are in Japan? Quite often the students are called by their school year and not by their exact age. Various types of media also use the Japanese school year system to break children up into groups.
You might, for example, see students referring to themselves and their friends by their school year in anime and manga. If you go to a theme park, rides often restrict children of certain school years from riding, whereas in Western countries usually the age is specified. This can be confusing if you didn’t grow up in Japan or are not aware of how the Japanese school system is organised. In this lesson then, let’s take a look at the ages corresponding to different school years, as well as the different types of school.
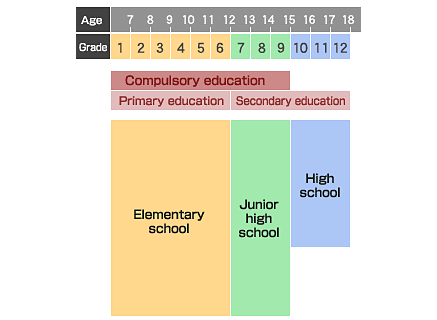
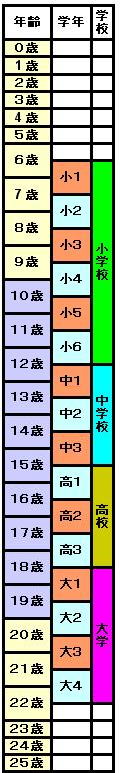
As you can see from the above charts, most Japanese school children begin their primary education when they enter elementary school at age 6. The Japanese school year begins in April, and children who have their 6th birthday on or before 1st April enter the first year of elementary school in the same year. A child born from 2nd April onwards would have to enrol in elementary school the following year when they are closer to 7 years old. Students in the first year of elementary school are referred to as 小学一年生 (しょうがく いちねんせい) or usually just 小1 (しょう いち). There are 6 years of elementary school.
Secondary education begins with junior high school at age 12. Students in the first year of junior high school would be 中学一年生 (ちゅうがく いちねんせい) or again, just the shortened form 中一 (ちゅう いち). There are 3 years of junior high school.
Compulsory education in Japan is known as 義務教育 (ぎむきょういく) and consists of the 6 years of elementary school plus the 3 years of junior high school – ages 6-15. Afterwards comes the second part of secondary education – high school. As you might guess, we label students in the same manner as before, so a first year student in high school would be 高校一年生 (こうこう いちねんせい) or just 高1 (こう いち). As with junior high school, high school consists of 3 years of education.
Many students also continue on to university. A first year university student would usually be 18 years old (providing they enter university immediately following high school). As before, a first year student would be 大学一年生 (だいがく いちねんせい) or just 大1 (だい いち).
Types of School
In order then, here are the main types of school you’re likely to encounter.
保育園
ほいくえん
Nursery School
Officially recognised, not as schools, but as welfare centres in order to provide basic education and support for children. Often used as day care centres by parents who cannot look after their infant children (0-5 years of age) full time due to work or other circumstances.
幼稚園
ようちえん
Kindergarten
Or ‘Pre-School’. In contrast to 保育園 above, 幼稚園 are officially recognised as a type of school under the School Education Law, and mainly provide a more structured education for children aged 3-5 years of age.
That’s not all! Log in to see the rest of this lesson.
Or if you aren’t a member yet, please consider signing up.
Leave a Reply